Mining pools: who mines Bitcoins today and how

In the world of blockchain, mining pools and mining farms are exactly the thing that supports the cryptocurrency value – a multi-million industry where hundreds of people are engaged. Bitcoin mining has become a mature business in China, Iceland, and Hong Kong today.
If you are interested in cryptocurrencies, you have probably seen articles telling about big farms, their scale is amazing. The industry is maintained by electronics manufacturers that develop advanced mining machines, electric power producers, employees of farms.
Mining pools are online communities of miners that jointly mine Bitcoin blocks. Both big farms and standalone miners unite into pools. By the way, today Bitcoin is not the most beneficial cryptocurrency for mining. It was outperformed by Sia(SC), Deutsche eMark(DEM), and Musicoin(MUSIC) that bring miners more than 100% of profit. However, the majority of pools mine Ethereum (ETH), Bitcoin (BTC), and BitcoinCash (BCH) as the most liquid ones. Detailed statistics is available on whattomine.com.
How a pool works
Let us shortly explain how blockchain and mining pools work.
Bitcoin network as any other cryptocurrency consists of blocks. It stores transaction records (user-to-user cryptocurrency transfers) and data of the last block encrypted as hash. More details about hash functions are available on CoinDesk. To continue functioning, blockchain should build new blocks.
As blockchains are decentralized systems, new blocks should be mined by the network in general rather than a single authenticating party. To decide on the new block, the network should reach a consensus. To reach a consensus, miners offer specific blocks, which are verified, and then the network eventually chooses a single block that will constitute the next part of the ledger. Its author receives a reward – an amount of cryptocurrency defined by the system. That is what mining is. Generally speaking, mining is the calculation of complex cryptographic tasks with combined efforts of all computers in the network.
The higher the computer capacity, the more solutions it offers and the higher the probability that it will get the reward. On average, the reward depends on the number of offered solutions. Therefore, to receive a high profit, miners create farms (an aggregation of high-power computers) and unite in pools. The operation principle of a pool resembles a torrent tracker: the total capacity of all miners participates in mining, so new blocks are found quickly. The reward is also distributed among all participants of the process.
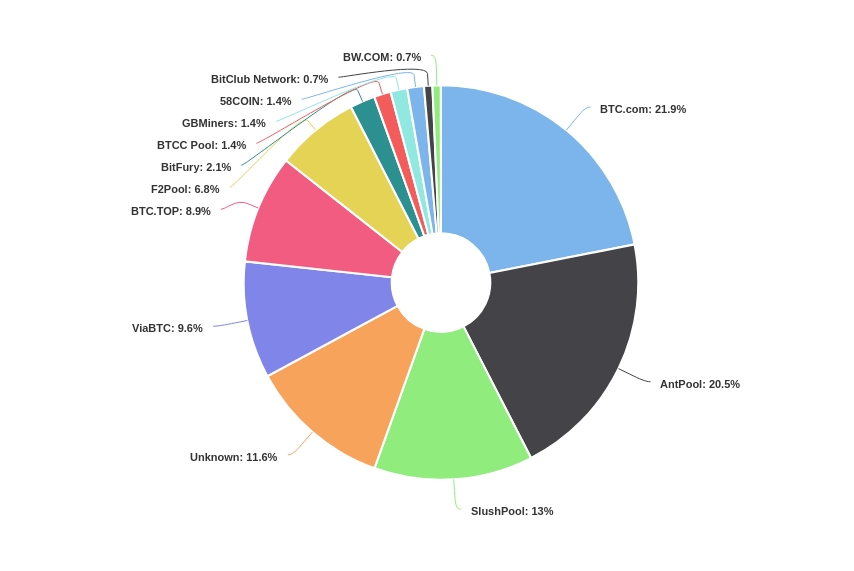
The largest pools: approximate estimation of hashrate distribution
Large pools: geography and peculiarities
China has the most developed mining infrastructure, so it is a home to the most large-scale mining farms and biggest pools. They are usually owned by the same companies. Chinese pools account for up to 60% of the global hash power; currently, the list of three biggest pools includes BTC and AntiPool, two Chinese pools.
The Czech Republic occupies a prominent position in the ranking of pools. That is where Slush Pool is based, the first mining pool in the history that currently occupies the third position in terms of the hash power.
Overall, there are around a thousand and a half of such servers; most of them specialize in Bitcoin, some mine Ethereum, and others mine several different tokens at once.
For instance, Slush Pool mines Zcash, among others.
It is not very important where a pool is located, as most mining companies rent servers in several countries, and miners from different countries join them. The main criterion for participants is not the location but a user-friendly interface and the algorithm of reward distribution.
Schemes of token distribution differ from server to server, but the main criterion remains unchanged almost everywhere – the computational power.
As blockchain grows, mining pools are getting more centralized: large associations receive a critical number of votes. That is the reason why the crypto community is considering the possibility of shifting to other algorithms that would not require high-power graphics processors for the generation of new blocks.




